 |  |
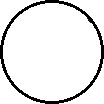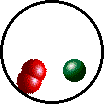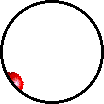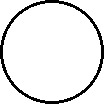
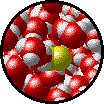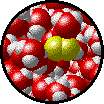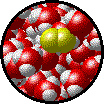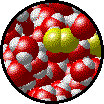
| Microscopic view of Br2 gas (solute) dissolved in Ar gas (solvent). | Microscopic view of Ar gas (solute) dissolved in liquid H2O (solvent). |
 |  |
| Microscopic view of Br2 liquid (solute) dissolved in liquid H2O (solvent). | Microscopic view of solid NaCl (solute) dissolved in liquid H2O (solvent). |
Solvent: the substance in which a solute dissolves to produce a homogeneous mixture, solvents can also be gases, liquids, or solids
source
Adsorption: the adhesion of molecules (or ions and atoms) to the surface of a solid or liquid. The molecules accumulate only at the surface and do not enter the bulk of the adsorbing material.
- Adsorbate: the substance whose molecules get adsorbed at the surface.
- Adsorbent: the substance on whose surface the process takes place.
- It is a surface phenomenon.
- Adsorbents substance: Alumina gel, Silica gel, Zeolites, Activated carbon, Graphite
- Desorption: the reverse process in which the adsorbed substance is removed from the surface of the adsorbent.
Absorption: the assimilation of molecular species throughout the bulk of the solid or liquid.
Gas-liquid absorption (a) and liquid-solid adsorption (b) mechanism. Blue spheres are solute molecules

